What is the meaning of CTP plate?
Aug. 06, 2025
CTP plate (Computer-to-Plate) is a printing plate that is imaged directly from digital files using laser or light sources, without the need for film. This technology has revolutionized the prepress workflow by improving the efficiency, accuracy, and environmental sustainability of offset and other plate-based printing methods.
CTP plate is the product of the Computer-to-Plate process, where digital images are directly imaged onto the printing plate. This modern method eliminates the need for intermediate film production, resulting in higher print quality, shorter turnaround times, reduced chemical usage, and lower overall costs in high-volume, high-precision printing applications.
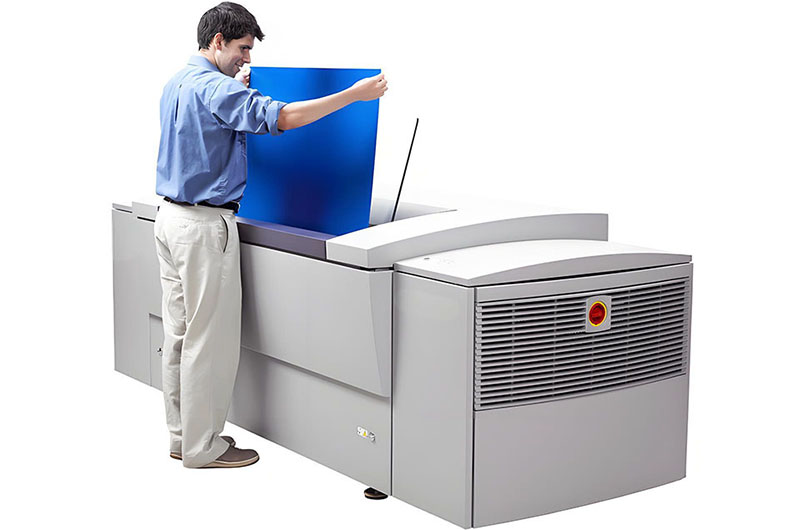

CTP stands for Computer-to-Plate, and CTP plate is the printing plate used in this digital imaging process. Unlike traditional film-based plate-making (such as Computer-to-Film or CTF), the CTP process transfers digital images directly onto the plate, significantly streamlining workflows in modern printing.
Types of CTP Plates
-
Thermal Plates
Use infrared laser on a thermal-sensitive coating. Highly durable, ideal for long-run printing.
-
Violet Plates
Exposed using violet laser (405–410 nm). Suitable for short to medium print runs, cost-effective.
-
Process-Free Plates
Do not require chemical processing, reducing environmental impact.
-
Photopolymer Plates
UV-sensitive, commonly used in flexographic printing for packaging and labels.
Different Types of CTP Plates
| Type | CTP Plate Image | Description |
| Thermal CTP Plate |

|
Thermal CTP Plates are sensitive to infrared laser energy. They are known for their high durability and excellent dot reproduction, making them frequently used in high-volume printing environments. Thermal plates come in single-layer and double-layer formats, with double-layer designs providing enhanced print stability and image quality. |
| Violet CTP Plate |

|
Violet CTP Plates are imaged using violet laser technology. They are generally more cost-effective and environmentally friendly. Although the image resolution may be slightly lower compared to thermal plates, violet plates require fewer chemicals, making them suitable for small to medium-sized printing businesses and cost-sensitive applications. |
| Process-Free CTP Plate |
|
Process-free plates eliminate the chemical development stage. During printing, the non-image areas are removed, reducing waste and operating costs. The image is directly presented on the plate and cleaned by the printing press, minimizing chemical waste and simplifying workflows. This type of plate is ideal for environmentally conscious printing companies seeking simplified production processes. |
| Positive and Negative Working Plates |

|
Positive plates dissolve upon exposure, mainly used for UV imaging plates, where exposed areas become blank. Negative plates harden upon exposure, commonly found in thermal plates, where exposed areas form the image. The choice between positive and negative working plates depends on the printing application, imaging method, and printing press compatibility. |
Comparison of Different Types of CTP Plates
| Parameter | Thermal CTP Plate | Photopolymer CTP Plate | Process-Free CTP Plate |
| Laser Type | Infrared Laser (830 nm) | Violet Laser (405 nm) | Infrared/Violet Laser |
| Development Process | Chemical Development (Some Require Baking) | Alkaline Developer | No Development Required |
| Print Run Durability | 100,000+ Impressions | 50,000-80,000 Impressions | 30,000-50,000 Impressions |
| Resolution | 2400-2540 dpi | 2400-3000 dpi | 2400 dpi |
| Environmental Impact | Medium (Requires Chemical Processing) | Medium (Requires Developer) | High (Zero Chemical Emissions) |
| Cost | High (Equipment + Consumables) | Medium | Medium to High (Higher Plate Cost) |
| Application Scenarios | Long Runs, High-Precision Printing | Medium to Short Runs, Fine Graphics | Short Runs, Eco-Friendly Printing |
How to Choose a CTP Plate?
- Choose Thermal CTP for Long Runs: Ideal for high durability and stability (e.g., packaging boxes, textbooks).
- Choose Photopolymer CTP for High-Precision Printing: Best for fine image reproduction (e.g., art books, luxury packaging).
- Choose Process-Free CTP for Eco-Friendly Needs: Suitable for meeting regulations or short-run quick printing (e.g., food labels, corporate brochures).
The selection of CTP plates requires balancing factors like print volume, resolution needs, environmental considerations, and budget constraints. Thermal plates are known for their durability, photopolymer plates excel in high-resolution applications, and process-free plates lead the trend of sustainable printing.
Common Specifications and Sizes of CTP Plates Offered by Haomei Aluminum
| Description | Size | Thickness |
| Process Less Plates | 335mm x 485mm | 0.12mm |
| Procesless Thermal CTP Plate | 510mm x 400mm | 0.15mm |
| Positive Thermal Plates | 650mm x 450mm | 0.15mm |
| Offset Printing Plates | 400mm x 514mm | 0.2mm |
| Offset Printing Plates | 310mm x 514mm | 0.2mm |
| Offset Printing Plates | 388mm x 495mm | 0.2mm |
| Offset Printing Plates | 469mm x 572mm | 0.2mm |
| Offset Printing Plates | 514mm x 388mm | 0.2mm |
| Offset Printing Plates | 308mm x 495mm | 0.2mm |
| Double Coating Layer (positive CTCP plate) | 745mm x 605mm | 0.2mm |
| CTCP Plates | 800mm x 1030mm | 0.28mm |
| CTCP Plates | 800mm x 1030mm | 0.3mm |
| CTCP Plates | 745mm x 605mm | 0.3mm |
| CTCP Plates | 1055 x 811mm | 0.3mm |
| CTCP Plates | 766mm x 605mm | 0.3mm |
| CTP Thermal Double Layer | 785mm x 1030mm | 0.3mm |
| CTP Thermal Double Layer | 790mm x 565mm | 0.3mm |
| CTP Thermal Double Layer | 790mm x 595mm | 0.3mm |
| Procesless Thermal CTP Plate | 650mm x 550mm | 0.3mm |
| UV CTP Plates | 1030mm x 785mm | 0.3mm |
| UV CTP Plates | 1050mm x 795mm | 0.3mm |
| Conventional CTP Plates | 740mm x 605mm | 0.3mm |
| Thermal Offset Plates (positive) | 750mm x 840mm | 0.3mm |
| CTP Plates Thermal Single Layer | 13 3/16" x 19 3/8" | 6ml |
| CTP Plates Thermal Double Layer | 13 3/16" x 19 3/8" | 6ml |
| CTP Plate | 104.5mm x 80.5mm | Customized |
| CTP Plate | 800mm x 600mm | 0.3mm |
| CTP Plate | 910mm x 665mm | 0.3mm |
| CTP Plate | 920mm x 760mm | 0.3mm |
| CTP Plate | 1030mm x 770mm | 0.3mm |
| CTP Plate | 1030mm x 790mm | 0.3mm |
| CTP Plate | 1030mm x 838mm | 0.3mm |
Types of CTP Plate Imaging Systems
- Internal Drum Platesetter: The plate is mounted inside a rotating drum, and a fixed laser or light source exposes the plate.
- External Drum Platesetter: The plate is wrapped around an external drum, and the imaging head moves along the drum to expose the image.
- Flatbed Platesetter: The plate lays flat, and a laser beam exposes it line by line.
These configurations impact speed, accuracy, and the maximum plate size that can be handled.
Advantages of CTP Plates
- Speed and Efficiency: Eliminates the film step, shortening prepress time.
- Cost Savings: Reduces expenses related to film, chemicals, and labor.
- Quality: Higher resolution, with sharper images and finer details since it avoids film-related degradation.
- Accuracy: Precise registration and dot reproduction, offering higher precision in aligning color separations on the plate.
- Sustainability: Less waste and fewer chemicals compared to CTF (Computer-to-Film).
CTP Plate Working Principle
- Digital Workflow: Digital files (e.g., PDFs) are processed through prepress software to create a rasterized image.
- Imaging: A platesetter (CTP machine) uses lasers (thermal, violet, or UV) to etch the image onto a photosensitive or thermal plate.
- Processing: The exposed plate may undergo chemical development (for conventional plates) or be process-free (for process-free plates).
- Printing: The plate is mounted on the printing press, where ink adheres to the imaged areas and is transferred to paper via rollers.
Direct Digital Imaging with CTP Plate:
In CTP, files from desktop publishing applications are sent directly to a dedicated imaging device (called a platesetter), which exposes the plate material. This bypasses the intermediate film-making step, reducing errors and improving image quality.
Applications of CTP Plates
CTP technology is widely used in newspaper, magazine, commercial, packaging, and label printing. It revolutionizes prepress workflows by reducing steps and enhancing quality and efficiency.
- Commercial Printing: Brochures, magazines, books.
- Packaging: Corrugated boxes, labels, flexible packaging.
- Newspaper: High-speed daily production.
- Industrial Printing: Decorative prints, textiles.
Considerations for CTP Plates
- Initial Investment: CTP equipment and platesetters are costly.
- Plate Handling: Photosensitive plates require careful storage and handling.
- Technical Expertise: Skilled operators are needed for workflow management and calibration.
Users viewing this material also viewed the following
Further reading: ctp platectp machinectp plate making machinecomputer to plate ctpctp plates for offset printingctp printingctp computerctp computer to platectp computer to plate machinectp machine for printingplate ctpctp printing platectp plate machine







