Types of Plates Used in Offset Printing A Comprehensive Guide
Jul. 25, 2025
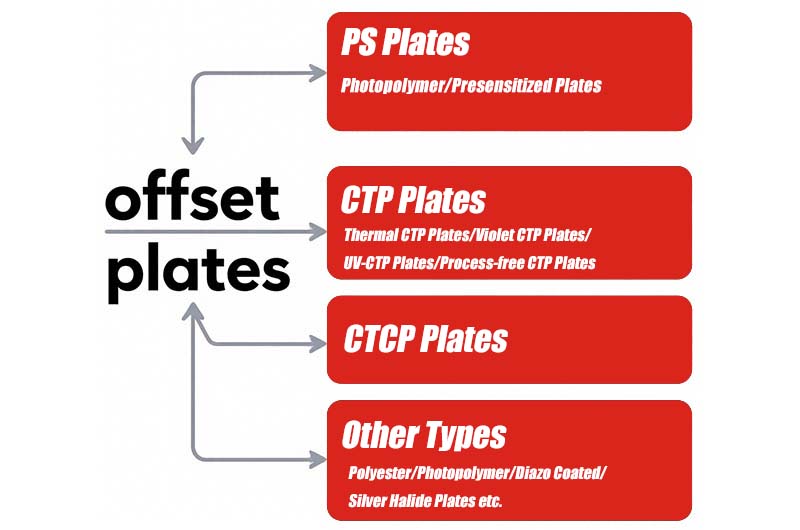
Currently, offset printing plates are mainly divided into three categories: PS Plates (Presensitized Plates), CTP Plates (Computer-to-Plate Plates), and CTCP Plates (Computer-to-Conventional Plate). These plates differ significantly in imaging principles, manufacturing processes, and application scenarios. Choosing the right plate is crucial for printing companies to improve efficiency and reduce costs.
- PS Plates, as a representative of traditional plate-making technology, have advantages such as low cost, mature process, and easy operation, but also have limitations including long plate-making processes, difficulties in quality control, and environmental pressure. PS Plates are mainly suitable for small printing companies, short-run printing, and printing tasks with low quality requirements.
- CTP Plates, as the mainstream technology in digital plate-making, offer high imaging quality, shorter process flow, and high automation, but come with higher equipment and plate material costs. Different types of CTP plates have their own features: Thermal CTP Plates are suitable for high-quality commercial and long-run printing; Violet CTP Plates are ideal for newspaper and general commercial printing; UV-CTP Plates are used in commercial sheet-fed and web press printing; Process-free CTP Plates offer advantages in environmental protection and simplified processes.
- CTCP Plates, as a hybrid technology, combine the advantages of CTP and PS Plates, featuring low cost, good compatibility, and ease of operation, making them especially suitable for small and medium-sized printing companies transitioning to digital workflows.
Offset Printing Plates Type
PS Plates (Presensitized Offset Plates)
PS Plates (Presensitized Offset Plates) are presensitized plates made of aluminum substrate with a photosensitive coating on the surface. Their basic structure mainly includes the following components:
- Aluminum Substrate: Typically made from 1050/1060 aluminum alloy, it undergoes electrolytic graining and anodizing to form a fine grain structure, providing good hydrophilicity and mechanical strength.
- Photosensitive Layer: Mainly composed of diazo photosensitive resin, it is the key part for image and text transfer on PS Plates.
- Protective Layer: Covers the photosensitive layer to protect it from damage during storage and transportation.
PS Plates are a traditional plate-making method, typically used for small-batch printing. They are generally more economical than CTP plates.
Features of PS Plate
- Mature plate-making process: PS Plate technology has been developed for many years, with a mature process and easy operation.
- Good dot reproduction: The fine grain structure and high resolution of PS Plates allow for 2%~98% dot reproduction.
- Easy ink-water balance: The hydrophilic part of PS Plates offers good hydrophilicity, wear resistance, and chemical stability.
- Strong adaptability: PS Plates can adapt to various types of printing machines and different printing substrates.
- Cost-effective: PS Plates are relatively inexpensive, and associated consumables like developer are also economical.
- Moderate print run durability: Without baking, standard PS Plates can withstand 30,000–80,000 impressions. After baking, the durability can increase to 200,000–300,000 impressions.
Limitations of PS Plate
- Complex plate-making process: PS Plate production involves multiple steps such as film output and plate exposure, resulting in a longer process and lower efficiency.
- Difficulty in quality control: The many intermediate steps may introduce issues like inaccurate dot linearity, leading to unstable print quality.
- Environmental pressure: The production process of PS Plates involves high power and water consumption and generates significant pollution.
- Limited flexibility: Once a plate is made, any content change requires remaking the plate.
- Inefficient for small runs: The setup costs for PS Plates are high, making small-batch jobs less economical on a per-unit basis.
- Not suitable for high-precision demands: PS Plates may fall short in applications requiring extremely high accuracy.
CTP Plates (Computer-to-Plate)
CTP (Computer-to-Plate) is a digital plate-making technology that enables direct imaging from digital files onto plates, bypassing the need for film output used in traditional CTF (Computer-to-Film). This significantly simplifies the production process.
Depending on the imaging technology, CTP plates can be divided into several types, including:
- Thermal CTP Plates
- Violet CTP Plates
- UV-CTP Plates
- Process-free CTP Plates
- Thermal CTP Plates: Use heat to form images, known for their stability and wide application, especially suited for high-quality commercial and publishing printing.
- Violet CTP Plates: Exposed using violet laser, offering fast speed and high precision.
- UV-CTP Plates: Use ultraviolet exposure, available in both positive and negative types.
- Process-free CTP Plates: Provide environmentally friendly solutions by eliminating the need for developer chemicals.
Features of Thermal CTP Plates
- Daylight operation: With low sensitivity to natural light and exposure by infrared laser, it can be operated under daylight conditions.
- Excellent dot quality: Based on threshold imaging, dot size is accurately reproduced with particularly sharp edges.
- Stable imaging quality: Requires a threshold energy level to form an image, ensuring consistent quality and stable publishing output.
- Good press performance: Excellent on-press stability, requiring minimal make-ready sheets to achieve ink-water balance.
- High print run durability: Excellent dot reproduction and high resolution; after baking, plates can achieve over 1 million impressions.
- User-friendly: Similar in feel and processing to traditional PS Plates, fully compatible with existing dampening solutions and press adjustment systems.
Features of Violet CTP Plates
- High resolution: Shorter violet laser wavelength enables higher resolution imaging.
- Fast exposure speed: Generally offers higher sensitivity, allowing for faster exposure.
- Good compatibility: Works with various photoinitiator systems.
- Relatively simple operation: Compared to other CTP technologies, easier to handle and doesn't require special environmental conditions.
Features of UV-CTP Plates
- High photosensitivity: Highly sensitive to UV light, enabling rapid exposure.
- Excellent dot reproduction: Capable of 2% to 98% @250lpi AM screen resolution and 25μm FM screen resolution.
- Outstanding print performance: Offers precise dot reproduction, excellent ink-water balance, and superior abrasion resistance.
- Environmentally friendly: Can be printed with eco-friendly UV inks, reducing emissions of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during printing.
- High adaptability: Compatible with mainstream UV-CTP plate-making equipment and developer solutions.
Features of Process-free CTP Plates
- Simplified Process: Eliminates post-processing, improves production efficiency, no need for chemical development, and reduces overall platemaking cost.
- Significant Environmental Advantages: No environmental pollution, and overall platemaking cost can be reduced by 35%.
- Improved Production Efficiency: No development processing required, significantly shortens platemaking time.
- Stable Quality: More direct imaging process reduces potential quality issues from intermediate steps.
- Reduced Operating Costs: Although the plate price is relatively high, the overall operational cost is lower.
Comparison of Various CTP Plate Performances
The following table compares the performance of several main types of CTP plates:
| Plate Type | Imaging Principle | Resolution | Operating Environment | Print Durability | Main Advantages | Main Limitations | Application Scenarios |
| Thermal CTP Plate | Thermal imaging using infrared laser | 0.5%-98% dot range | Daylight operation | Over 1 million impressions after baking | Excellent dot quality, stable imaging, good printing adaptability | High equipment cost, expensive plates | High-quality commercial printing, long-run printing, fine printing |
| Violet Laser CTP Plate | Free radical polymerization triggered by violet laser | Up to 300 lpi | Darkroom or safe light required | 250,000–400,000 impressions | Fast exposure speed, high resolution, good compatibility | High environmental requirements, needs special processing | Newspaper printing, general commercial printing, packaging printing |
| UV-CTP Plate | Photochemical reaction initiated by UV light | 2-98% @ 250 lpi | Safe light operation | 100,000 impressions without baking, over 500,000 after baking | High sensitivity, good dot reproduction, environmentally friendly | Requires dedicated developer, high processing demands | Commercial sheetfed and web offset printing, UV ink printing |
| Process-free CTP Plate | Physical or thermal reaction to form ink-receptive layer | Depends on specific type | Daylight or safe light | 300,000–600,000 impressions | No development, environmentally friendly, simple workflow | High plate price, technology not fully mature | Environmentally demanding printing, high-efficiency production, long-run printing |
CTCP Plates (Computer-to-Conventional Plate)
CTCP (Computer-to-Conventional Plate) is a hybrid technology that combines the advantages of CTP technology with traditional PS plates. Its core feature is using conventional PS plates as the plate material while employing computer-to-plate digital imaging, thereby retaining the benefits of traditional PS plates and achieving the high efficiency and quality of digital platemaking.
CTCP plates bridge the gap between traditional PS plates and digital CTP plates. They use a process similar to CTP but are designed to be compatible with conventional platemaking equipment.
Advantages of CTCP Plates
- Significant Cost-efficiency: Eliminates film output and exposure steps in traditional processes, saving consumables and related costs.
- Improved Print Quality: Inherits CTP system advantages and reduces quality issues from intermediate steps.
- Simplified Workflow: Direct from computer to plate, eliminating film output and exposure steps.
- Stable Quality: More accurate than traditional analog platemaking, with clearer dot reproduction.
- Fast Return on Investment: Much lower investment cost compared to CTP systems, with short payback period.
Limitations of CTCP Plates
- Relatively Slower Speed: Compared to high-end CTP systems, platemaking speed is usually slower.
- Limited Resolution: While adequate for most print needs, typically lower than high-end CTP plates.
- Technology Maturity: Relatively new, not yet as mature as traditional CTP in some aspects.
- Equipment Compatibility Limits: May require modification or upgrade of existing equipment in some cases.
- Long-term Consumable Cost: High exposure energy demand may lead to increased light source replacement.
CTCP Plate Compatibility with Traditional Platemaking Equipment
One of the greatest advantages of CTCP plates is their high compatibility with traditional platemaking equipment. This compatibility is mainly reflected in the following aspects:
- Plate Compatibility: Uses standard PS plates as the printing material, no need to change plate types.
- Developer Equipment Compatibility: Compatible with traditional PS plate developing machines.
- Chemical Compatibility: Uses the same developer and other chemicals as traditional PS plates.
- Post-processing Compatibility: Compatible with same post-processing techniques such as retouching, baking, and gumming.
- Workflow Compatibility: Seamlessly integrates with existing CTF workflows, allowing gradual transition to digital workflow.
Other Types Offset Printing Plate
Polyester Plates / Photopolymer Plates / Diazo Coated Plates / Silver Halide Plates / Waterless Plates / Electrophotographic Plates / Hybrid Plates
| Type | Characteristics | Applicable Range | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Photopolymer Coated | Coated with photopolymer; highly durable and suitable for long-run printing. | High-volume printing, multi-color printing | Strong durability, clear images. | Relatively high cost, requires precise handling. |
| Diazo Coated | Coated with diazo compounds; suitable for short-run printing. | Short-run printing, small volume printing | Low cost, simple to operate. | Poor durability, lower resolution. |
| Silver Halide | Coated with light-sensitive material; suitable for short-run single-color printing. | Single-color printing, small volume printing | High image quality, low cost. | Not suitable for color or high-volume printing. |
| Electrophotographic | Uses toner technology; suitable for two-color printing. | Short-run two-color printing | Low cost, fast processing. | Average quality, limited to low-volume jobs. |
| Waterless | Coated with a silicone layer; no water is used. | High-quality, eco-friendly printing | High quality, eco-friendly, low ink consumption. | High cost, requires specialized equipment. |
Photopolymer plates are coated with a layer of polymer material that hardens when exposed to ultraviolet light. These plates are widely popular due to their excellent durability, capable of handling print runs of up to one million impressions. Their wear resistance and high-quality image reproduction make them an important choice in the printing industry.
Applications:
- Large-scale printing jobs
- Multi-color printing
- Commercial printing production
Advantages:
- Extremely durable, with excellent wear resistance
- Suitable for long-run printing jobs
- High-quality image reproduction, with clear details
Disadvantages:
- Higher initial investment compared to diazo plates
- Requires precise exposure and development techniques to ensure optimal results
Diazo coated plates are coated with a photosensitive organic compound called diazo. These plates are highly suitable for short-run printing, typically supporting up to 250,000 impressions. Due to their simple structure and low cost, diazo coated plates are ideal for projects that do not require long-term plate use or large-scale printing.
Applications:
- Short-run printing
- Single-color printing jobs
- Low-cost small to medium-volume printing
Advantages:
- High cost-effectiveness for short-run printing
- Simple processing and handling
- Suitable for low-demand printing projects
Disadvantages:
- Poor durability compared to other plate types, especially for long-run printing
- Limited to relatively lower resolution prints
Silver halide plates are coated with light-sensitive materials, similar to the emulsion used in photographic film. When exposed to light, the silver halide coating undergoes a chemical reaction. These plates are mainly used for short-run printing, particularly for single-color jobs. In the post-processing stage, the silver coating is removed, leaving the desired image.
Applications:
- Short-run printing, typically supporting a few thousand impressions
- Single-color printing jobs, particularly those requiring detailed images
Advantages:
- Provides high-quality images and details
- Fast processing, simple to operate
- Cost-effective for small printing jobs
Disadvantages:
- Only suitable for single-color printing
- Not suitable for high-volume printing
- Requires specialized processing equipment
Electrophotographic plates use a technology similar to that of toner-based printers, where the image area is specially treated to attract toner-like ink. These plates are typically used for two-color printing and can be inserted into printing copiers for efficient print performance. The electrophotographic process makes them particularly effective in short-run printing and projects with lower color complexity.
Applications:
- Two-color printing
- Short-run copying jobs
- Fast-turnaround simple printing projects
Advantages:
- Suitable for digital printing environments
- Cost-effective for small-volume, limited-color printing projects
- Fast processing, easy setup
Disadvantages:
- Not suitable for high-quality or full-color printing
- Only suitable for low-volume printing jobs
The distinctive feature of waterless plates is that they do not require water to restrict ink to the image area. Instead, the plate surface is treated with a special silicone resin that effectively prevents ink from entering the non-image areas. Since no water or chemical fountain solution is used, this process is more environmentally friendly.
Applications:
- High-quality color printing
- Environmentally friendly printing practices
- Printing jobs requiring precise color control and clear details
Advantages:
- No need for fountain solution, reducing chemical waste
- Provides high print quality, especially in details and color reproduction
- Shorter drying times, lower ink consumption
Disadvantages:
- Higher cost, requires specialized processing
- Requires more precise handling and setup
Offset Printing Plate Selection and Application Recommendations
Plate Selection Guide for Different Printing Needs
Selecting Plates by Print Volume
- Short-run printing (1,000–10,000 impressions): Recommended ordinary PS plates or CTCP plates for low cost and suitable for small batches.
- Mid-run printing (10,000–50,000 impressions): Recommended CTCP plates or UV-CTP plates for balanced cost and quality.
- Long-run printing (over 50,000 impressions): Recommended thermal CTP plates or process-free CTP plates for high durability and reduced plate changes.
Selecting Plates by Print Quality Requirements
- General quality: Recommended ordinary PS plates or CTCP plates for low cost and meeting basic print needs.
- Medium quality: Recommended violet laser CTP plates or UV-CTP plates for moderate resolution and good cost performance.
- High quality: Recommended thermal CTP plates or high-precision process-free CTP plates for excellent dot quality and stable imaging.
Usage and Maintenance Recommendations for Offset Printing Plates
Plate Storage Conditions
- Storage: Store in 10–30℃ environment with relative humidity not exceeding 65%, avoid direct sunlight and humidity.
- Unsealing and Handling: Open and handle under safe light, wear clean gloves when handling plates to avoid direct finger contact with plate surface.
- Pre-use Inspection: Check plate surface for scratches, stains, or other defects, and confirm size and type compliance.
Platemaking Process Control
- Exposure Control: Set exposure parameters according to plate type and printing requirements; regularly check the output strength of exposure equipment.
- Development Control: Use matched developer solution, control development temperature and time. PS plate development temperature is generally 23±2℃.
- Post-processing Control: Plates should be thoroughly washed after development. When baking plates, strictly control temperature and time. PS plate baking temperature is generally 220–240℃.
Why Photopolymer Plates are the Most Popular Choice
Despite the availability of various plate types in the market, photopolymer coated plates remain the most commonly used choice in offset printing.
- Durability: Photopolymer plates have excellent wear resistance, making them ideal for high-volume and long-run printing jobs.
- Versatility: These plates perform excellently in both single-color and multi-color printing, catering to a wide range of project needs.
- Print Quality: Photopolymer plates can produce fine details and clear images, which are crucial for high-quality printing work.
For these reasons, photopolymer plates are a reliable and versatile choice for many commercial printing companies, especially in industries that require consistency and durability.
Users viewing this material also viewed the following
Further reading: ctp plates for offset printingctp offset machinectp offset printingctp offset printing plates